COMPETENCY-BASED
CURRICULUM IN KENYA: GRADES 7 TO 9
Kenya's education system was altered with
the introduction of the Competency-Based Curriculum. Replacing the traditional
8-4-4 system, CBC focuses on skills, attitude, and application of knowledge
rather than rote memorization. It aims at preparing the learner to face
challenges of the 21st century by fostering the development of individual
talents, critical thinking, and problem-solving. The Junior Secondary School
phase, comprising Grades 7 to 9, is a vital component of this system, acting as
a transition point where learners deepen their understanding, explore diverse
disciplines, and build on foundational skills acquired in earlier grades.
CURRICULUM
STRUCTURE AND OBJECTIVES
In the CBC framework, Grades 7 to 9 focus
on molding learners' talents and preparing them for advanced education and
careers. The curriculum provides opportunities to explore multiple learning
areas while promoting holistic development. Core subjects include Mathematics,
English, Kiswahili, Science, Social Studies, and Religious Education.
Additionally, optional subjects such as visual arts, music, home science, and
technical education allow learners to pursue interests and talents.
Key objectives at this stage are the
development of critical thinking, collaboration, and fostering creativity.
Learners are normally involved in practical activities, group projects, and
research-based tasks that emphasize the use of knowledge in real
situations.
The
Role of Pathways in CBC
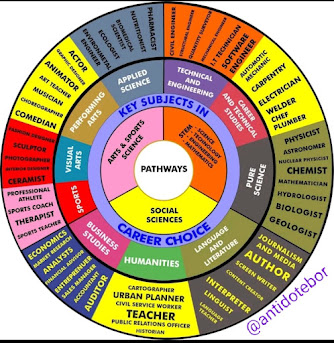
A unique element of Grades 7 to 9 is the
pathways that take learners into specializations and fields of interest and
aptitude. The three pathways are:
1.
Arts and Sports Science
This is for learners who have talent and interest in creative and
sporting disciplines. It has subjects such as visual arts, performing arts,
music, and physical education.
2.
Social Sciences
With a focus on humanities, this strand encompasses such disciplines as
geography, history, religious studies, and social ethics.
3.
Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM)
For learners leaning toward technical and scientific fields, this strand
encompasses advanced mathematics, applied sciences, and computer studies.
Pedagogical
Approaches
The CBC focuses on the following
learner-centered teaching approaches:
- Project-Based
Learning: Learners work on projects that require research, teamwork, and
problem-solving, often culminating in presentations or prototypes.
-
Inquiry-Based Learning: This approach encourages
learners to ask questions, investigate solutions, and build knowledge through
exploration.
-
Practical Assessments: Emphasis is placed on
hands-on activities, such as experiments, artistic creations, and technical
tasks, to enhance learning by doing.
These strategies ensure that the learners
acquire both theoretical understanding and practical skills and attitudes
necessary for personal and societal development.
Assessment
in CBC
The CBC adopts a continuous assessment
instead of an over-reliance on standardized examinations. Learners are thus
assessed based on their performance in class activities, projects, portfolios,
and formative assessments. By the end of Grade 9, learners undergo summative
assessment to determine if they are ready for engagement in Senior Secondary
School. Besides, the assessment is accompanied by a record of performance of
the learner in different subjects and co-curricular activities.
The shift in assessment methods means that
there is less pressure resulting from examinations and that assessments will
give a more actual reflection of the capability of a learner and his
progress.
Challenges
in Implementing CBC for Grades 7 to 9
While CBC has its merits, it faces
numerous challenges that are prevalent in Kenya. These are:
1.
Infrastructure: Some schools do not have prior
facilities such as laboratories, workshops, and libraries to execute practical
learning.
2.
Training of Teachers: Not all teachers undergo
complete training on CBC approaches, and at times this negatively reflects in
teaching.
3.
Parental Engagement: The curriculum demands
parental involvement in supporting learning even at home, which could be an
uphill task for some families, either because of the pressures of modern life
or other resources constraints.
4.
Resource Availability: Learning materials,
including textbooks and equipment for practical lessons, are often inadequate
or maldistributed.
5.
Equity Issues: Rural and less-well-off schools face
challenges in meeting the demands of CBC owing to a lack of funding and
infrastructure gaps.
The
Way Forward
In light of these challenges, the Kenyan
government and stakeholders have taken the following measures, among others:
- More money invested in the
infrastructural development of schools.
- More frequent training for teachers on
how to deliver CBC.
- Sensitization for parents on their role
in the new education system.
- Collaboration with private companies in
resource and technological provision for disadvantaged schools.
Conclusion
The CBC for Grades 7 to 9 represents a
bold step in the direction of a more inclusive, practical, and skills-based
education system in Kenya.
In focusing on the holistic development of
learners, it aims at creating future-ready individuals who can thrive in varied
fields. However, this sustained effort calls for investment and collaboration
by all stakeholders to overcome the challenges in the implementation of the
CBC. As Kenya continues on this transformative journey, the Junior Secondary
phase remains a cornerstone in shaping the nation’s educational landscape.

No comments:
Post a Comment